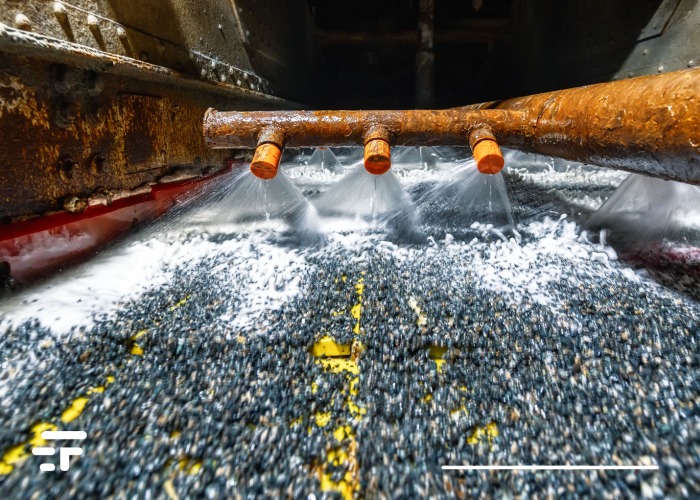

Biological nanofibrils effectively extract precious metals from water
A new system could greatly simplify access to precious metals that are essential for many modern industrial processes and appliances.

A new system could greatly simplify access to precious metals that are essential for many modern industrial processes and appliances.

UV light and aluminum chloride as a catalyst can break down polystyrene into a chemical used in perfumes and medicines.
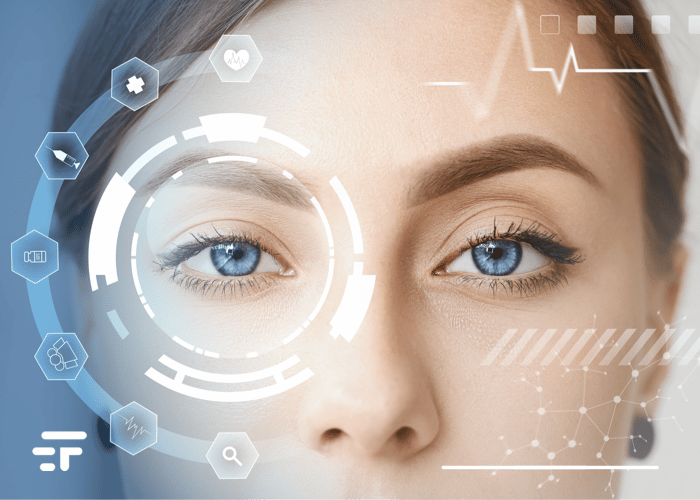

A team of researchers and entrepreneurs has developed an implant, made from pig skin, that mimics the human cornea: it works great
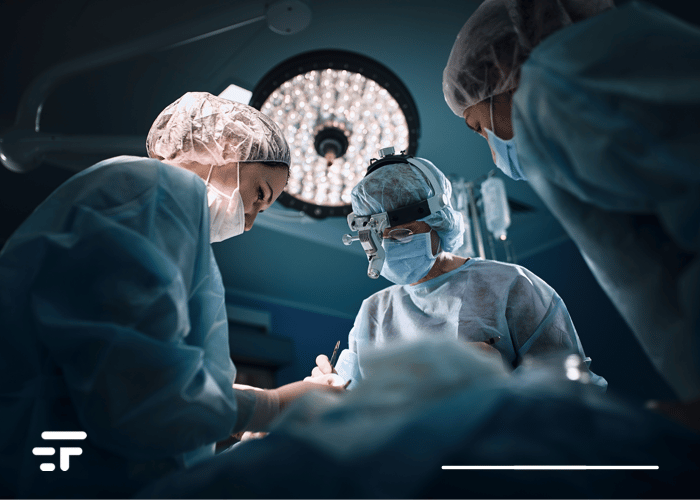
Artificial blood can repair cell damage caused by lack of oxygen. It could make transplants easier, treat heart attacks and strokes, and even reverse cell death.
Pig cells today, but tomorrow this experimental technique could preserve human organs destined for donation
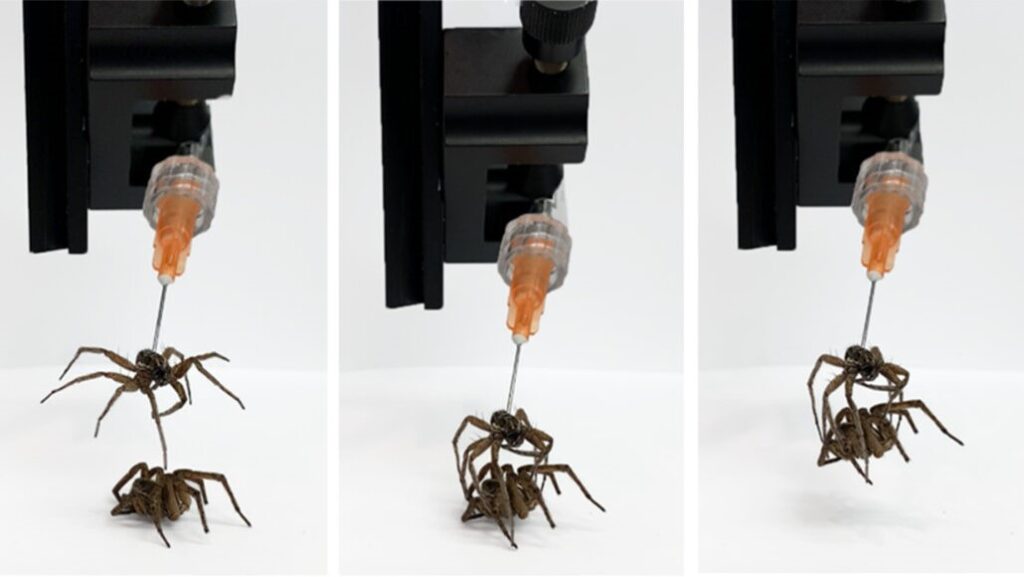

A new field of study known as "necrobotics" is born. Researchers used dead spiders to grab objects
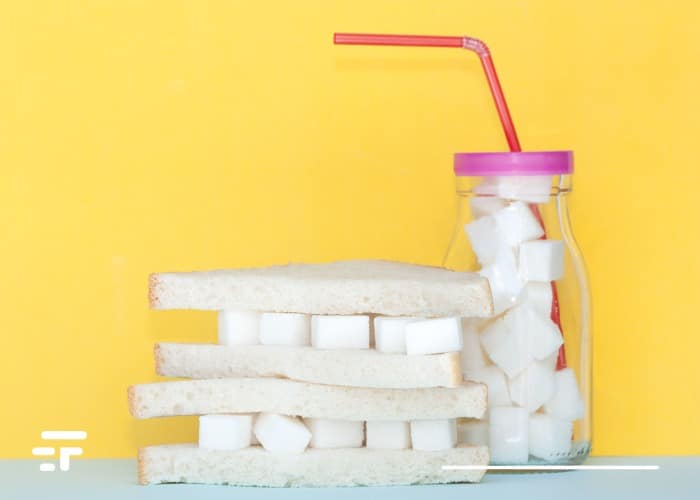

According to a study published by Cambridge, over the past 10 years there has been an ever-increasing use of added sugars and non-nutritive sweeteners in the production of packaged foods.
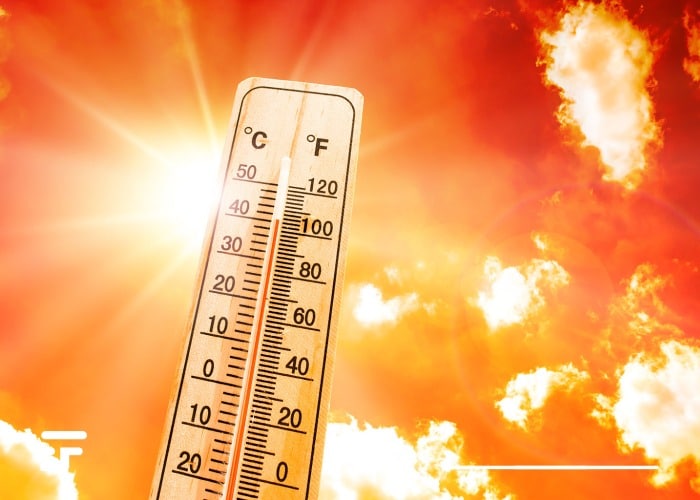

If true, millions more people could be at risk from heat waves and dangerously high temperatures.

A new genetic modification can increase photosynthesis and uptake of fertilizers in rice, wheat and other crops. The effect is a 40% higher yield with reduced curing times.

A molecule identified in mice, purine inosin, which stimulates fat burning in brown adipocytes. Human tests are near.

Aerosols (and clouds) forming in the Arctic produce effects on the rest of the planet: here are the efforts to understand which and how many are
Harvard bioengineers developed the first biohybrid model of a human ventricle with beating and aligned heart cells.

The University of California develops high-density batteries that withstand very hot and very cold temperatures without batting an eye.
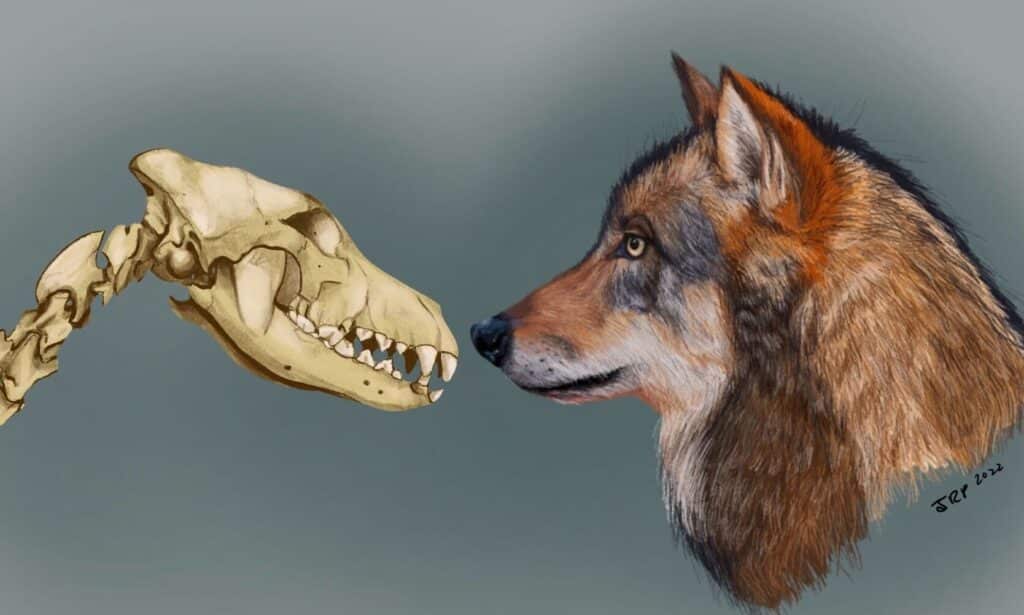

A study by some geneticists and archaeologists has shown that the lineage of man's best friend, the dog, can be traced back to at least two specific populations of ancient wolves. Finally we will be able to find out how (and where) we went from the wild wolf to the domesticated dog.

The discovery of a mechanism to repair the heart muscle has the potential to revolutionize heart treatments and cures

All over the world it is hunting for bacteria and insects that consume waste to dispose of it. The last one? A "super" worm hungry for polystyrene.

Over 300 infections in 21 countries outside Africa. Should we worry? How fast is its spread? We assess the situation

First phase of testing for a new drug based on monoclonal antibodies: rectal cancer "totally eliminated" in 100% of patients.

A 'photonic' chip, which uses light to process, is able to recognize billions of (small) images per second.